NASA’s Perseverance rover has identified a unique rock formation in the Jezero Crater on Mars, strongly suggesting it is an iron-nickel meteorite – an object originating from outside the planet. The discovery, made after more than five years of exploration, adds another piece to the puzzle of Mars’ geological history and provides further insight into the types of materials that have impacted the red planet over billions of years.
An Unusual Find in Jezero Crater
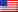
The rock, dubbed “Phippsaksla,” stands out from its surroundings due to its composition and shape. Measuring approximately 80 centimeters (31 inches) wide, it appears larger and more sculpted than other rocks in the area. The rover’s Mastcam-Z cameras captured detailed images, while the SuperCam instrument used lasers and spectrometers to analyze its chemical makeup.
What Makes It a Meteorite?
The key indicator is Phippsaksla’s high iron and nickel content. These materials are common in the cores of large asteroids, which formed as heavy minerals sank toward the center during the early stages of the solar system. Iron-nickel meteorites are relatively rare compared to stony meteorites, making this discovery particularly noteworthy.
Why This Matters
Meteorites provide valuable clues about the composition of asteroids and other celestial bodies in the solar system. By studying Phippsaksla, scientists can gain a better understanding of the types of materials that have bombarded Mars over time. This also helps refine models of planetary formation and the evolution of the solar system.
Perseverance’s Role in Martian Exploration
Perseverance is equipped with advanced instruments that allow for detailed on-site analysis. The rover’s SuperCam can remotely measure the chemical composition of rocks, while its onboard drill enables the collection of samples for future return to Earth.
The Future of Martian Sample Return
While Perseverance has collected numerous rock samples, their return to Earth requires a separate mission. NASA is planning a future spacecraft to retrieve the samples, which will then be analyzed in laboratories with more sophisticated equipment.
Implications for Martian History
The discovery of Phippsaksla is not entirely surprising, as iron-nickel meteorites have been found on Mars before. However, each new find adds to the growing body of evidence that Mars has been subjected to impacts from space over billions of years. This has likely played a role in shaping the planet’s geology and potentially even its habitability.
The Perseverance rover continues to explore the Martian surface, uncovering new clues about the red planet’s past. Its discoveries, including Phippsaksla, will contribute to a deeper understanding of Mars and its place in the solar system